Definition
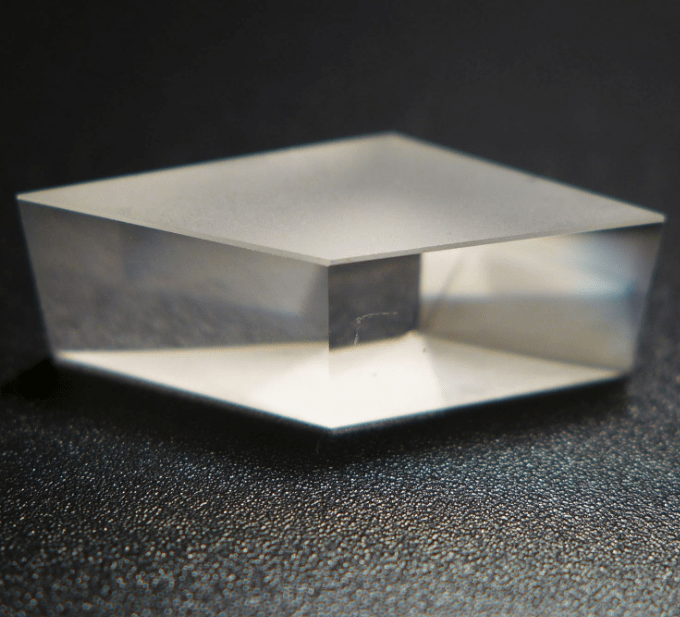
Rhombic prism, a reflective prism with a rhombus cross-section. A pair of angles of the rhombus is 45°, which can actually be used as a combination of two rotating prisms and rectangular transparent glass. Light is incident from one end at an angle of 45°, undergoes total reflection on the other side, forms a 90° deflection, reaches the other side in a direction parallel to the incident side, undergoes total reflection again, and exits in a direction parallel to the original light ray.
Features
- Beam splitting and separation
- Can be coated for polarization separation
- Rhombic Prisms are offered as uncoated
- Coatings are available upon request
Rhombic prisms are used to displace a beam laterally without changing its direction. They may be coated to transmit part of the beam and produce two parallel and displaced emerging beams.
Material
Can be coated to produce a polarizing beam separator. These prisms are manufactured from either BK7A or Fused Silica.
Coating
They are supplied uncoated but many coating options are available.
Application
Rhomboid prisms are commonly used to deflect laser beams without changing their direction. In imaging applications, rhombus prisms will shift the optical axis without flipping the image. The lateral displacement is equal to the length of the prism (specified in dimension D).
Bote rhombus prisms have highly accurate angles, ensuring that the parallelism between the output beam and the input beam is within 30 arc seconds, and are suitable for use in some situations that require position deviation.
| Material: | BK7A UV Fused Silica |
| Surface Flatness: | < λ / 8 @ 633 nm |
| Surface Quality: | <20/10 |
| Dimension Tolerance: | < + 0.00 / – 0.20 mm |
| Angular Deviation | < 2 arc min |
| Clear Aperture: | > 85% in central circular dimension |
| Bevel: | 0.3 mm (typical) x 45° |