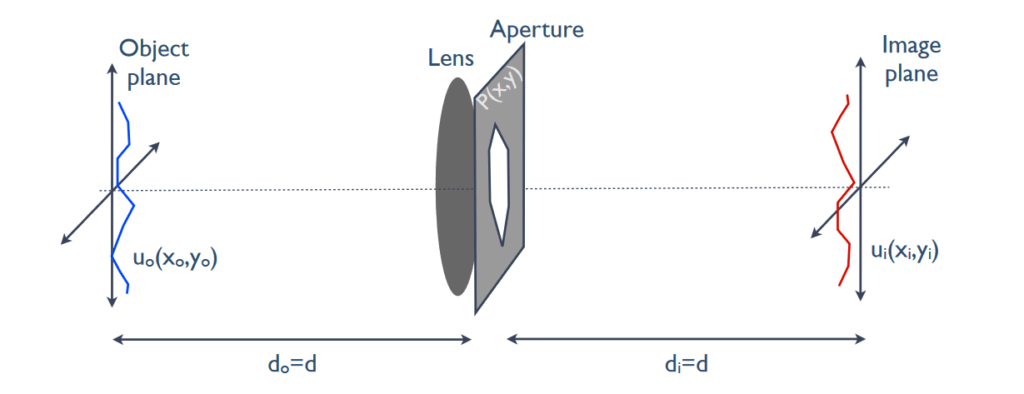
After the invention of the laser in the 1960s, which gave people access to new coherent light sources, Fourier optics has developed rapidly in both theory and application. Fourier optics uses Fourier spectrum analysis methods and linear system theory to provide new interpretations of a wide range of optical phenomena. Its main contents include scalar diffraction theory, lens imaging rules, and the use of spectrum analysis methods to analyze the properties of optical systems, etc.
How to calculate Fourier focal length?
The Fourier expansion coefficient formula is a0=π square/3. The Fourier expansion refers to the form expressed by a trigonometric series, that is, the Fourier series of a function converges to the function itself. A name for the time.
The Fourier expansion coefficient formula is a0=π square/3. The Fourier expansion refers to the form expressed by a trigonometric series, that is, the Fourier series of a function converges to the function itself. A name for the time.
Fourier focal length refers to the focal position of a lens or mirror and can be calculated by the following formula: F = 1 / (2πf), where F is the Fourier focal length and f is the focal length of the lens or mirror. The calculation of Fourier focal length is based on the principle of Fourier optics, which describes the focusing effect of light after passing through a lens or mirror. The calculation of Fourier focal length is very important for optical design and optimization of imaging systems, and can help determine the position and parameters of lenses or mirrors to achieve the desired imaging effect.
What is optical transformation?
The use of modern optical information processing technology is one of the important development directions of current remote sensing image processing.
Optical information processing usually uses the two-dimensional Fourier transform ability of thin lenses to use coherent light (laser) or partially coherent light (white light). In the optical information processing system, the film image is subjected to optical Fourier transformation to transform the space. The image in the frequency domain is converted into information in the frequency domain, and then the image is enhanced by “modifying” the spectrum – filtering. Therefore, the essence of optical information processing is optical transformation processing based on Fourier optical theory.
BOTE Fourier Lens
BOTE has the ability to design and process various optical lenses according to your requirements. Please feel free to contact us if any related questions.